The evidence that the big bang may be real...
Doppler Effect
- If something is emitting waveforms and stationary, there is no Doppler effect.. duh
- If something is emitting waveforms and moving relative to an observer, then the wavefronts gets changed depending on the direction of the observer.
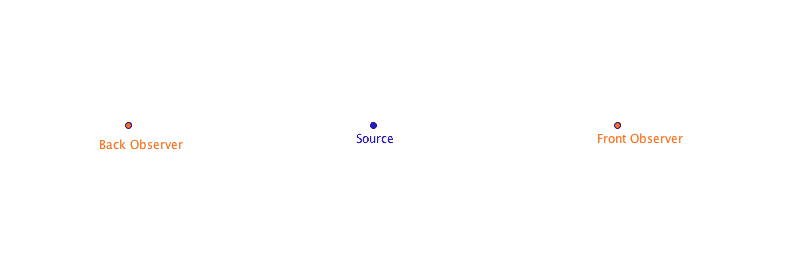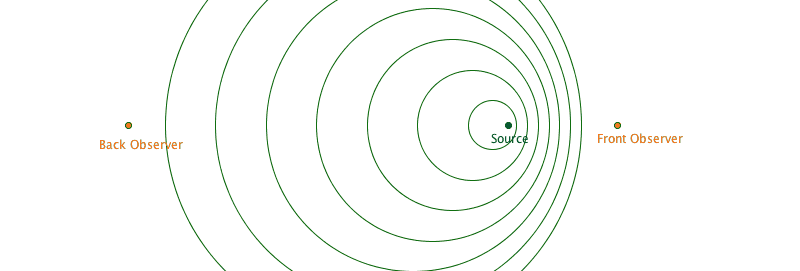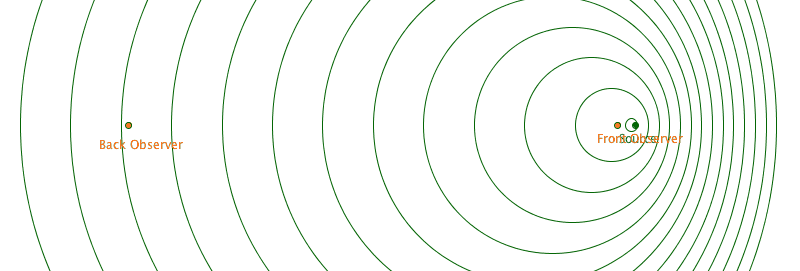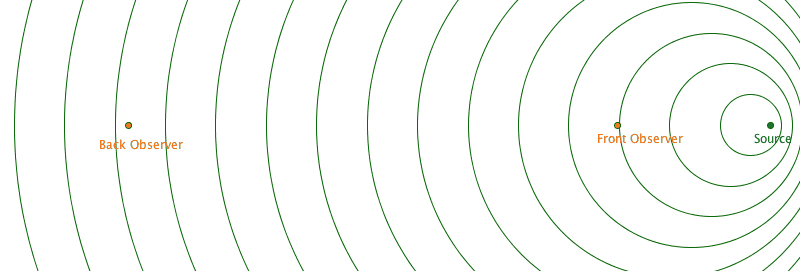
This was first figured out for sound. But since light have wave-like properties, then light can also do this!!!!
But to get an appreciable shift from the Doppler effect, the source must be moving quite fast.
Note that if its going at the same speed as the wavefronts propagate, you get a bunch of interference, called a sonic boom. (boom boom) (only for sound duh top ten questions why cant things with mass go at the speed of light!?!??!?!1)

And then, if you go even faster (only for sound lol) you get funny cones.

Doppler effect but light
- If light is coming from an object moving away from us, its wavelength is increased. The light is considered redshifted.
- If it is moving towards us, it is decreased. This light is considered blueshifted.
- This doesn't mean it becomes red light or blue light, but instead, it is shifted towards the red end of the spectrum.
Spectral lines are fr
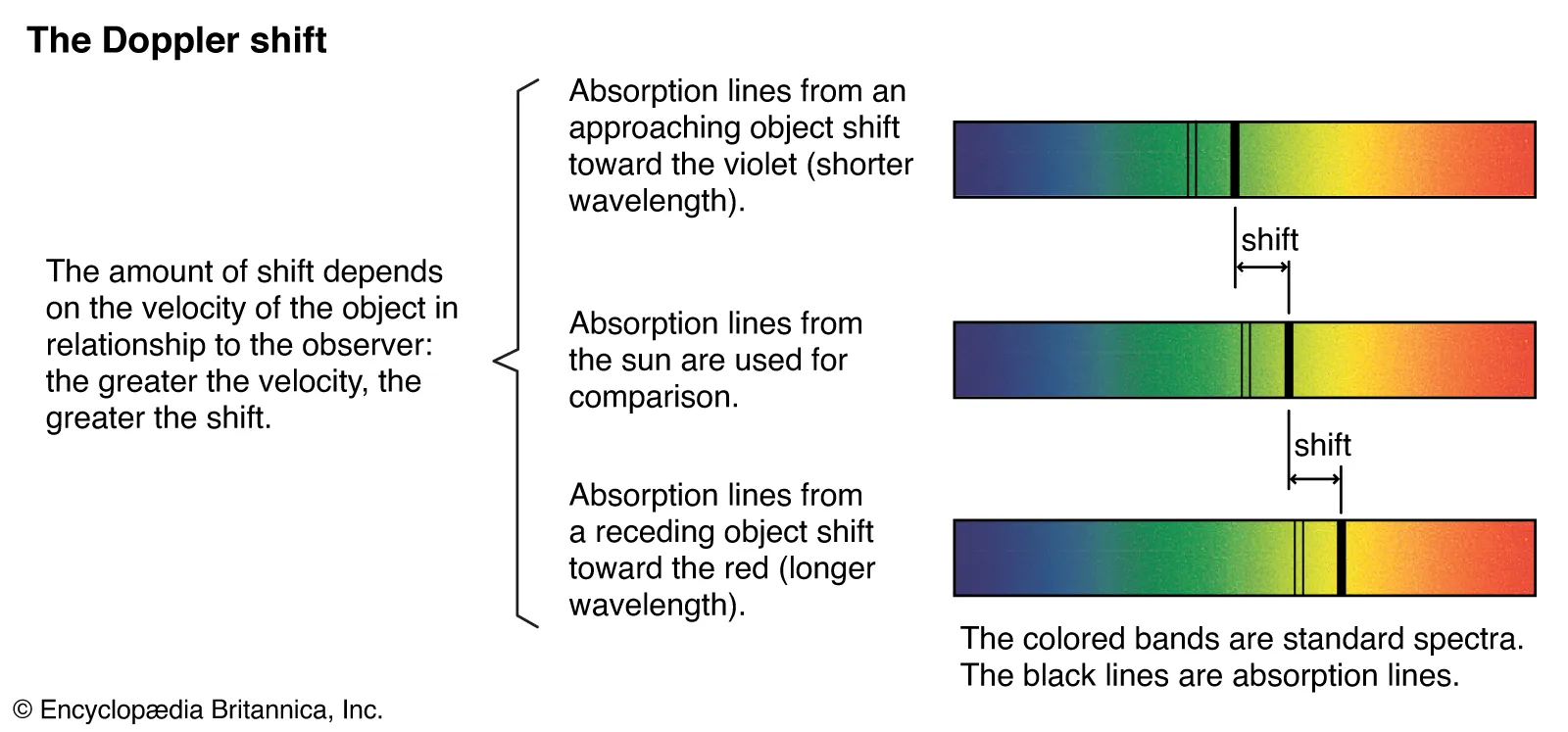
- From a stationary observer and from a stationary source (relative), we get the normal emission spectrum.
- In contrast, all wavelengths become longer if the light is redshifted. Thus, we can determine the object is moving away from us. Likewise for if the light is blueshifted.
- This is useful for determining whether stars are moving towards or awar from us!
Hence, if we can detect these lines and compare them with our own, we can get a sense of which way our neighbouring friendly objects are going! (Hubbling time)
A few definitions about astronomy
- 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) refers to the mean Earth-Sun distance. i.e. $1.496 \times 10^8km$.
- 1 Light year refers to the distance that light travels in a vacuum in a year. This is not a measure of time!
- Secret trick:
- For a particle moving at 0.xx c, the time in years it travels for a distance written in ly is: $\frac{ly}{0.xx \ c}$
- 1 ly = $9.46 \times 10^{12}km$
- Note that 1 Parsec is 3.25 ly, while a Megaparsec is $\times 10^6$ times that.
- Parsecs were mostly used by Hubble. This is why its used in Hubble's law (Shock)
Measuring distance with angles and eyes
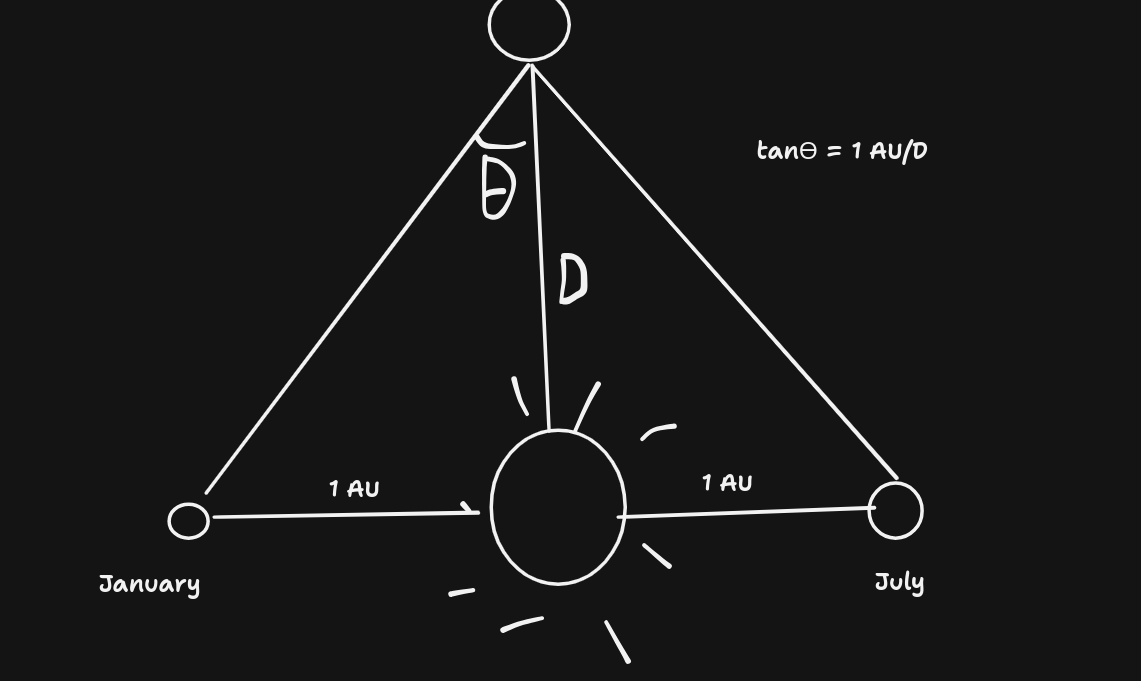
- Note that here, $\theta$ is called the parallax angle (oh my god chemistry reference!!?)
- This only works for reasonably close objects.
- Now, if $\theta$ is equal to 1 arcsecond, i.e. $\frac{1}{3600}$ of a degree, then the distance $D$ is what we consider to be 1 Parsec!
i.e. 1 Parsec = $\frac{1.496 \times 10^8}{\tan\left( \frac{1}{3600} \right)}=3.09\times 10^{13}km$ (Can use a similar calculation to find it in ly)
Back to Hubble's law
- Doppler effect on light
- Source moving away - redshift ($\lambda$ increases, $f$ decreases)
- If its moving towards - blue shifted
- It has been observed that the vast majority of galaxies were redshifted. This meant that the majority of galaxies were moving away from us. (This seems rather odd...)
- The further away a galaxy is, more redshift is observed.
So Hubble collected some data, and found that its literally a straight line!
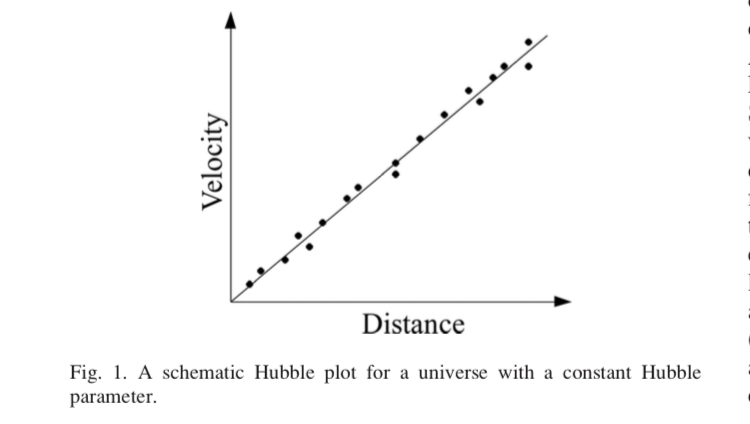
He realised that the galaxies were moving away from us at velocities which are proportional (Hubble's constant, $H_{0}$) to their distance from us!!!!?!?
And thus:
$$\begin{align}
v= H_{0}d
\end{align}
$$
(my mind is blown)
Here, $H_{0}=71kms^{-1}MPc^{-1}$. If you're doing a question, you gotta convert these things to get $\frac{1}{H_{0}}$... why would you want $\frac{1}{H_{0}}$? To be shown soooon.
SO what does Hubble's law indicate? The universe is expanding!!! But its not that stuff expands into places with stuff in there already. Space itself is literally expanding as a finite thing growing in space which is unknown.
This is opposed to the idea that expansion requires matter production. Why? No clue.
The endgame
Thus, the only way to explain Hubble's law is the Big Bang. i.e. all space, matter (and time) originated from an infinitesimally small singularity.
But there's a few other things that suggest the Big Bang:
- Expansion
- Cosmic microwave background radiation
- Expansion then contraction (big crunch)
- Steady rate of expansion
- Accelerated expansion $\checkmark$ (??? that's what the recent stuff suggests)
- Dark energy, dark matter, 92%
\begin{align}
E&=\frac{mc^2}{\sqrt{ 1-\frac{v^2}{c^2} }} \
\text{For }v=c, E&=\frac{mc^2}{\sqrt{ 1-\frac{c^2}{c^2} }} \
&=\frac{mc^2}{\sqrt{ 1-1 }} \
&=\frac{mc^2}{0} \
\text{Hence for }m\neq 0,E&= \infty \text{ which is impossible.}
\end{align}
$$$$





