Characterised by $-NH_{2}$ functional group.
They have primary and secondary formats. We don't need to understand how it works, but we do need to know that it's different from alcohols.
e.g. propan-1-amine, propan-2-amine (both still primary!)
Could be cause less molar mass $\implies$ less electrons, hence weaker dispersion forces
Could also be because of overlap of electron clouds results in reduced dispersion force + bent shape $\implies$ harder to stack and condense $\implies$ lower intermolecular force
Primary? "
Primary amines have one carbon bonded to the nitrogen. Secondary amines have two carbons bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines have three carbons bonded to the nitrogen." From here
Amines are weak bases.
$$CH_{3}NH_{2} + H_{2}O \rightleftharpoons CH_{3}NH_{3}^{+} + OH^{-} $$$\alpha$ amino acids
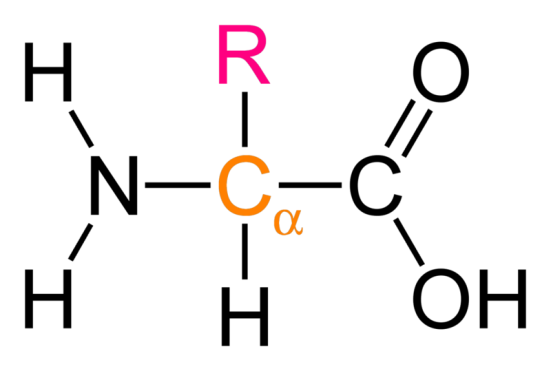
Will return to this later.
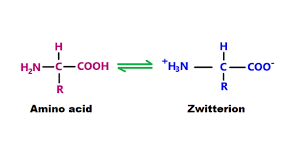
Primary is generally what we will focus on
Like a carboxylic acid but the OH is replaced with an amine!
Ethanamide
Secondary is out of the course, but it has the wacky N(yes, capitalised!).
Hydrogen bondind - usual properties
Amide MP/BP > Amines
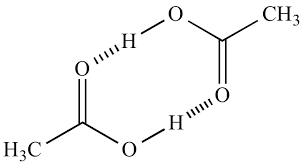
Dimer: when you get two hydrogen bonds back to back, usually made by amides/carboxylic acids.