task---
title: "Medical Physics and Dosimetry"
Key definitions
- Radiopharmaceutical: a pharmaceutical with a radioisotope attached, which are used to treat or diagnose specific diseases. The pharmaceutical part dictates where the radiopharmaceutical as a whole travels (as it interacts like the original pharmaceutical). The radioisotope decays, producing radiation which is used for medical imaging or radiotherapy.
Gamma Cameras
A gamma camera is a machine that is able to detect and make images from the very small amounts of ionising radiation emitted from patients having a nuclear medicine study.
Procedure
- A tracer (radioisotope attached onto a molecule/compound) that emits gamma radiation (woah its as if its in the name!?!)
- We usually use Technetium-99m or Thalium-201 as the radioisotope.
- The radioisotope-containing molecules/compounds are moved through a specific biological process to a specific part of the body.
- Again, the type of tracer determines where the tracer ends up, hence we use different tracers for different sites of the body!
- These tracers then emit a gamma ray which passes through the body and is picked up by the gamma camera.
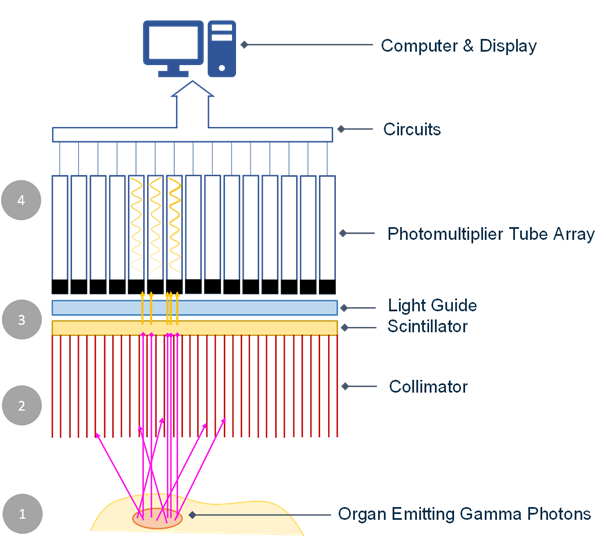
Gamma camera head
- The gamma rays enter the collimator.
- A thick plate of lead or tungsten riddled with a large number of very thin parallel channels.
- Only gamma rays parallel to the chanells can pass through.
- The channels point towards the body, and the lead + tungsten absorb any erroneous gamma rays travelling at a non-parallel angle.
- Gamma rays that pass through the collimator are met by the scintillating crystal, which blocks gamma rays and converts some of their energy into scintillations.
- Scintillations are bursts of light.
- This conversion is how the rays are detected!
- The scintillating crystall is made of sodium iodide, and is doped with thallium. It is sealed away from external light.
- Doping: introducing impurities to change electrical/optical/structural properties
- Photomultipliers then convert the scintillations into electrical signals.
- An electronic system for detection uses the electrical signals to find the position of the source of the gamma rays. Hence, after multiple scintillations are produced, the location of the tracer can be deduced.
An important distinction!
- Gamma cameras takes around 20 minutes to image and throughout this time the tracer is moving throughout the body.
- Hence we can observe how the tracer (more specifically the molecule it is attatched to) is being processed by the body.
PET Scans
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear medicine functional imaging technique that is used to observe metabolic processes in the body, and diagnose diseases and cancers.
-
Tracers: A molecule/compound with a radioisotope attached to it.
- Same thing as radiopharmaceutical, but not necessarily attatched to a medical component, instead attached to something the body uses (e.g. glucose).
-
The radioisotopes used in PET scans are usually isotopes with small half-lives such as $C-11$ ($\approx$ 20min), $N-13$ ($\approx$ 10min), $O-15$ ($\approx$ 2min), $F-18$ ($\approx$ 110min) etc.
- Short half-lives are used so that each scan requires less time and that a proper scan can be carried out within an appropriate time.
-
The PET scan uses a large donut-shaped machine containing gamma ray detectors.
Procedure
- Patient injected with a small amount of the tracer (the-radioisotope).
- The most common example of a tracer for PET is FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose, i.e. $F-18$ added to a glucose molecule).
- Based on the type of tracer, and the biological interactions it has with the body, it will build up in different paths of the body.
- This allows us to target specific parts of the body, i.e. by using tracers that we know build up the area of interest!
- i.e. We know glucose builds up in the brain. Hence, FDG is used to target the brain!
- The radioisotope within the tracer then emits positrons via beta + decay.
- Within a distance of 1mm, released positrons encounter an electron, annihilating and producing two gamma rays in the opposite direction.
- These gamma rays are detected by the PET scanner (large machine with donut-shaped hole) via a circular array of detectors.
- The data from the detectors is sent to a computer which then is able to reconstruct an image of the target area.
Reconstruction
-
When two gamma rays arrive at the exact opposite ends within a very small time difference, we can assume they are the result of the positron-electron annihilation created by the radioisotope. Hence, they are measured and we calculate that their origin is the midpoint between the two lines.
-
Gamma rays that do not have a corresponding gamma ray at the exact opposite end, or are not detected within the small time period, are ignored as "non-pair gamma rays".
-
Through the millions of legitimate gamma ray pairs produced by the tracer, we can create an iamge of the distribution of the tracer, hence we can recognise how the main molecule/compound is being used in the target area.
-
We can compare this image to that of a normal human being's, hence we can identify areas of abnormally high/low activity, hence diagnose illness.
-
We also use PET alongside CT so we can get "metabolic" and "anatomic" information
-
The image created is made of multiple colours each representing a value of SUV (standard uptake value). The standard uptake value measured dose uptake ratio. A 0 SUV is black and a 15 SUV is red. 0 corresponds to no activity, 15 corresponds to high.
Imaging
- 好处/利
- Non-invasive - no need to probe(?) the patient
- Can study how biological processes are working, hence can predict diseases before severe changes to the body occur, i.e. quicker diagnosis
- Radioisotopes used have small half-lives, so they do NOT build up in the body!
- 坏处/弊
- For PET, the production of positrons is dangerous as they can interact with tissues/living parts of the body and cause damage or cancer.
- Only a few times, else too much exposure to radiation!
- EXPENSIVE
Use of Radioisotopes in therapeutic treatments
There are two main ways radioisotopes can be used as treatments in medicine: either externally or internally.
Externally is called "teletherapy" or "external irradiation", and internally is called "brachytherapy" or "internal radionuclide therapy".
Teletherapy
-
Radiation is delivered from an external source, and is directed to the area of interest (usually an area with cancerous cells). Of which, there is only the Gamma Knife!
-
Gamma Knife is a procedure commonly used to treat brain tumours through high intensity gamma radiation.
-
The Gamma Knife usually has 201 Cobalt-60 sources, which are arranged hemispherically. The Cobalt-60 undergoes gamma decay.
-
The sources are positioned such that the gamma rays target a specific point in the patient. The patient is held in place so that the gamma rays hit the right spot.
-
The combined intensity of the individually low intensity gamma rays only the target point received a large dose.
-
Hence, this point is ionised through the radiation (hopefully the cancer cells) and dies (w).
Brachytherapy
- Radiation is delivered from sources that are as close as possible to the target site. There, the radiation from the source decaying will kill the targetted tissue (wording good!)
- We want to use BETA - EMITTERS (radioisotopes that undergo beta - decay), they have relatively low penetration ability, but relatively high ionisation ability, in comparison to gamma rays.
- We do not use alpha emitters. They are too ionising!
We split brachytherapy into 4 different types:
- Interstitial
- Inserting needles/wires inside the area of interest (the tumour). Sometimes they don't have to be removed.
- Intracavitary
- Placing a source of radiation, known as an applicator, into body cavities.
- This is so the walls of the cavities are exposed to radiation. After which, the applicator is always removed!
- Intraluminal
- Placing the applicator into hollow organs, then removing once specific dose is delivered.
- Intravenous (the big one)
- Radiopharmaceuticals travel through the body to the area of interest (the tumour). They then decay and thus ionise and kill the surroundings (hopefully killing the tumour).
- We can transport the radioisotope to the location either by having the radioisotope as an element following its usual biological path, or as a pharmaceutical.
Radioisotope production for medicine
- Produced locally(in the country)
- Neutron-rich - Too many neutrons, must Beta - decay
- Proton-rich - Too many protons, must Beta + decay
- ANSTO - Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation
We produce medical radioisotopes via the following ways:
- Cyclotron
- Nuclear reactor
- For neutron rich isotopes
- Electron accelerators
- Expensive, but another way to make proton rich isotopes.
Cyclotron is less dangerous(can be easily shut off), and it is the only thing that can produce Beta + isotopes!
In contrast, nuclear reactors produce a large amount for cheap!
Cyclotron
- Protons are accelerated in a spiral(circular) pathway towards the targeted material(usually something initially quite stable)
- Proton is accepted into the nucleus. e.g. bombardment of Oxygen-18
$$\begin{align}
_{8}^{18}O+_{1}^{1}p\to_{9}^{18}F+_{0}^{1}n \\
_{9}^{18}F\to_{8}^{18}O+_{+1}^{0}e
\end{align}
$$
Nuclear Reactor
- Stable isotopes bombarded by neutrons produced by nuclear reactor (i.e. fission of Uranium-235)
- For example, we want to produce Technetium-99m. We start with Uranium Silicide, which is eventually processed into Molybdenum-99, which is undergoes Beta - decay into Technetium-99m.
Electron Accelerators
- Bombard with photons
- Photons made by directing electron beam(a stream of electrons) from a particle accelerator onto a heavy metal.
- This produces "Bremsstrahlung radiation", i.e. the radiation given off by free electrons that are deflected (i.e., accelerated) in the electric fields of charged particles and the nuclei of atoms.
- Subjecting a target material to Bremsstrahlung radiation can result in a neutron being displaced.
$${42}^{100}Mo + \text{Photon}\to{42}^{99}Mo+_{0}^{1}n$$
Proton and neutron therapy
Proton therapy uses protons as the form of radiation.
-
It is more precise (???) than other forms of radiotherapy.
-
Protons irradiate at a lower depth, so less is scattered into healthy tissue.
-
Able to adjust speed.
-
Hence, we use for high required dose, but we don't want to kill the surrounding organs!
-
Positived charge damages DNA, intending to kill target cells (usually cancers).
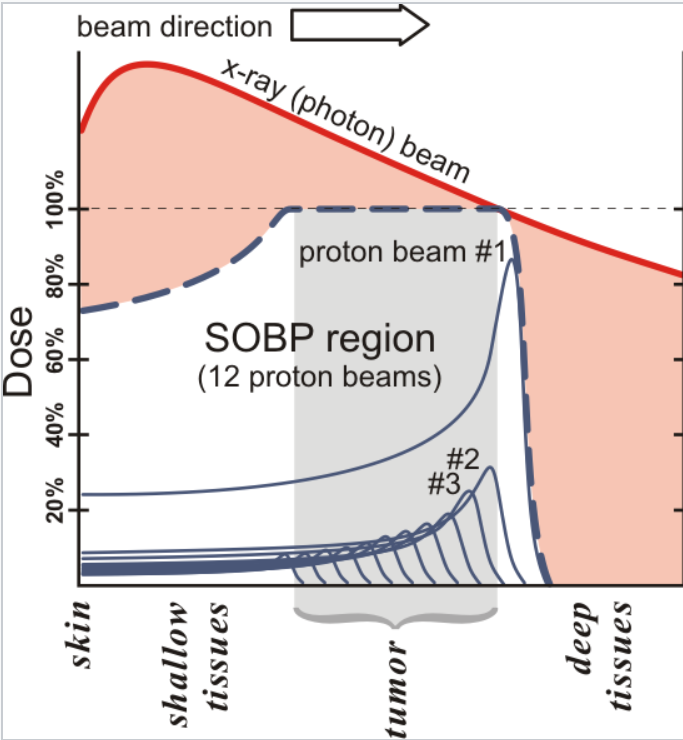 Here the SOBP region represents the combined radiation from multiple proton beams. By varying the depth of the proton radiation, we can more effectively target the tumour, in comparison to alternative radiotherapies such as x-ray. The red area represents additional affected tissues.
Here the SOBP region represents the combined radiation from multiple proton beams. By varying the depth of the proton radiation, we can more effectively target the tumour, in comparison to alternative radiotherapies such as x-ray. The red area represents additional affected tissues.
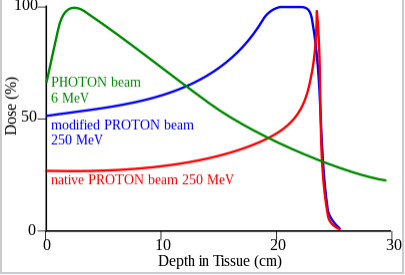
Neutron therapy has two types: fast neutron therapy and boron neutron capture therapy. Both involve the use of neutrons for medical purposes.
**While Gamma Knife/electron therapies kill cancers by ionising through free radicals (specifically of oxygen)(low LET), proton/neutron therapy kills via "nuclear interactions"(presumably proton/neutron capture) **
Neutron Therapy
- Used for specific diseases that are "radioresistant"; they are not easily removed by conventions forms of radiotherapy.
- Fast neutrons quite damaging (high quality factor), but do not damage cells equally!
- This means for some diseases, they are more sensitive to fast neutrons than surrounding healthy tissue, meaning a lethal dose for the diseased tissues may not be lethal for the healthy tissue.
- TLDR, for some unknown magical reason, cancerous cells are more affected by fast neutrons.
- Much more efficient, so dosage required is less (1/3 apparently) than the other forms of radiation therapy.
- Salivary gland tumours.
Quick important note
- The previous forms of radiotherapy produce low amounts of "linear energy transfer"(LET) radiation. LET refers to the amount of energy transferred to the material from an ionizing particle. This is in contrast to the usual method of ionizing such that free radicals were produced. Proton/neutron therapy rely on high-LET
- Hence, we use proton/neutron therapy for cases which might be resistant to low-LET radiation, i.e. not entirely affected by the production of free radicals.
- e.g. Melanoma, Renal cell carcinoma, Gastrointestinal cancer, Sarcoma
MASSIVE DETAIL
- proton - for more precise
- neutron - for more precise, but better than proton, as it can attack radioresitant cancers!
- all about oxygen - we use neutron when cancer does not have high concentrations of oxygen, which would ionise into free radicals and blow things up
Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (not needed)
- Boron radiopharmaceuticals injected into body.
- Boron has high affinity for "capturing" neutrons
- Fire an epithermal neutron beam
- "epithermal neutron beam" $\implies$ very shallow fr
- Boron absorbs neutrons from the neutron beam (preferential delivery)
- It then undergoes alpha decay.
$$\begin{align}
_{5}^{10}B+_{0}^{1}n\to_{5}^{11}B \\
_{5}^{11}B\to_{3}^{7}Li + _{2}^{4}\alpha
\end{align}
$$
-
This means we have targetted alpha decay, and it is fully controlled (we can turn off the beam at any time). We get all the benefits of alpha radiation (high ionizing), but few of the drawbacks! (active alpha radiation in your body).
The TLDR express of dosimetry
When us organic beings are exposed to ionising radiation, this causes cells to be damaged as it ionises atoms into free radicals! This can disrupt cell processes, causing damage or death to cells.
This is generally how cancer is produced from radiation, i.e. if DNA is ionised then it may cause mutations that lead to the cell becoming cancerous.
Summary of types of decay per procedure
Tables of tracers/radioisotopes
PET
| Tracer |
Area |
| FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose) |
Brain |
- Note the isotope is Fluorine-18
Gamma Camera $^{99m}_{43}Tc$
| Tracer |
Area |
| MDP (methyl diphosphonate) |
Bone |
| MAG3 (mercaptoacetyltriglycine) |
Renal (Liver) |
| MIBI (methoxy isobutyl isonitrile) |
Heart |
| Tetrofosmin |
Heart |
Gamma Knife
- It's just $^{60}_{27}Co$...
Brachytherapy
| Radioisotope |
Area |
| Iodine-131 |
Thyroid cancer (gland of the throat) |
| Iridium-192 |
Head and breast, or generally (to kill stuff) |
| Iodine-125, Palladium-103 |
Early stage prostate cancer |
Cyclotron
- Fluorine-18
- Carbon-11
- Gallium-67
- Bromine-77
- Rubidium-81
- Iridium-111
- Iodine-123
- Thalium-201

 Here the SOBP region represents the combined radiation from multiple proton beams. By varying the depth of the proton radiation, we can more effectively target the tumour, in comparison to alternative radiotherapies such as x-ray. The red area represents additional affected tissues.
Here the SOBP region represents the combined radiation from multiple proton beams. By varying the depth of the proton radiation, we can more effectively target the tumour, in comparison to alternative radiotherapies such as x-ray. The red area represents additional affected tissues.